In today's digital age, online payment processing has become an integral part of modern commerce. Whether you're shopping online, using a mobile app, or making a payment at a physical store, various entities work together seamlessly to ensure smooth and secure transactions. In this article, we'll delve into the roles of essential players in the payment ecosystem: Acquirers, Issuers, Cardholders, Processors, and PayTabs
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Video Tutorial
To understand the main key players in online payment processing, you can watch this video or read the following article.
Ecommerce Transaction flow
Chech the below chart that will help you understand how the e-commerce transaction flow works among the various key players.
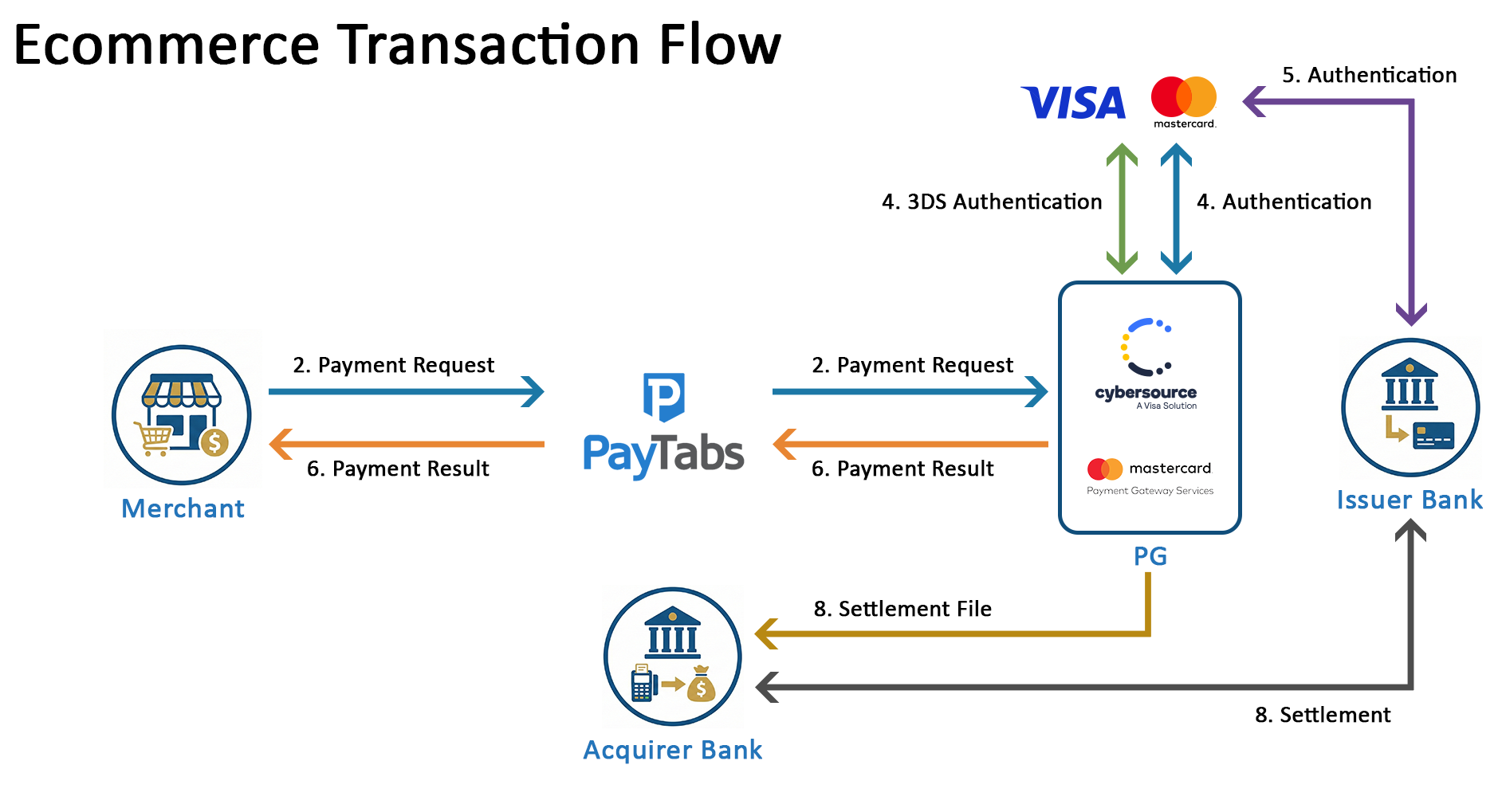
Main Key players:
1. Acquirer:
The acquirer, also known as the acquiring bank or merchant acquirer, plays a crucial role in facilitating electronic transactions for merchants. When a customer makes a purchase using a credit or debit card, the acquirer acts as an intermediary between the merchant and the cardholder's issuing bank (issuer).
Examples of (electronic transactions): swiping a debit card at a store, paying for a purchase online, or transferring money from an app to your bank account.
Process:
- The cardholder initiates a payment by providing their card details during checkout at the merchant's website.
- The merchant's payment system sends the transaction details to the acquirer for processing.
- The acquirer then forwards the transaction request to the card network (such as Visa or Mastercard, etc.…).
- The card network routes the request to the cardholder's issuing bank.
Key Responsibility for the Acquirer:
- Verifying and authenticating the transaction details.
- Requesting authorization from the cardholder's issuing bank to complete the transaction.
- Transferring the funds from the cardholder's account to the merchant's account after the transaction is approved.
- Managing the merchant's relationship and providing support for payment-related matters.
2. Issuer:
The issuer is the financial institution that provides credit or debit cards to consumers (cardholders). It is responsible for issuing and managing the cards, as well as overseeing the cardholder's account.
Example of - financial institution: The most common types of financial institutions include banks, credit unions, insurance companies, and investment companies.
Key responsibilities of the issuer:
- Setting the credit limit for credit cards or maintaining the available funds for debit cards.
- Providing customer support and handling inquiries related to the cardholder's account.
- Assigning credit and debit cards to approved cardholders (That is to say, the issuing bank is a consumer's credit or debit card issuer and manager)
- Approving or declining transactions based on the cardholder's available credit or funds.
3. Cardholder:
The cardholder is the customer who owns and uses the credit or debit card to make purchases or payments.
Key responsibilities of the cardholder:
- Safeguarding the card from unauthorized use or theft.
- Monitoring card transactions regularly to identify any fraudulent activity.
- Reporting lost or stolen cards to the issuing bank promptly.
- Managing credit card balances and making timely payments to avoid penalties.
4. Processors:
Payment processors are entities that act as intermediaries between the merchant, acquirer, and cardholder. Their primary role is to handle the technical aspects of the transaction. Payment processors securely transmit transaction data between the various parties involved, ensuring that the process is smooth and secure.
Processors also assist in fraud detection, risk management, and ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations. They play a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the payment ecosystem and protecting all parties involved from potential risks.
Key responsibilities of the processors:
- Act as intermediaries between merchants, acquirers, and issuers.
- Handle the technical aspects of payment transactions.
- Securely transmit transaction data between all parties involved.
- Assist in fraud detection, risk management, and compliance with industry standards and regulations.
5. PayTabs:
PayTabs is a secure payment processing company that facilitates payments for startups, entrepreneurs, SMEs, merchants, and super merchants by providing ecommerce, mobile commerce and social commerce invoicing and payment solutions, PayTabs acts as an interface between the merchant's website and the acquirer.
How PayTabs works:
- When a customer makes an online purchase, PayTabs securely collects and encrypts the payment information.
- PayTabs then forwards the encrypted transaction data to the acquirer for further processing.
- The acquirer communicates with the card network and the issuing bank to obtain transaction authorization.
- Once approved, PayTabs notifies the merchant, allowing them to proceed with the order fulfillment.
Conclusion
In the world of online payment processing, multiple players work together to ensure that transactions are smooth, secure, and efficient. Acquirers act as intermediaries between merchants and cardholders, while issuers validate and approve transactions. Payment processors, like PayTabs, play a vital role in handling the technical aspects and ensuring a safe payment experience for all parties involved. Understanding the roles of these key players enhances our appreciation of the complex and interconnected world of online payments.
Was this article helpful?
That’s Great!
Thank you for your feedback
Sorry! We couldn't be helpful
Thank you for your feedback
Feedback sent
We appreciate your effort and will try to fix the article